Learn More About
Treating Addiction
Opioid addiction is a form of drug abuse where one is dependent on opioid drugs and can’t function normally without them. It is the most common form of drug addiction in America and in many countries today. The high numbers are significantly contributed by the many opioid drugs in the market. Generally, opioids harm your health, especially your mental health.
Opioids are found in prescription drugs and are used as pain relievers.
Opioids are meant to be used for a short period, but people misuse them due to the intoxicating feeling that accompanies pain relief. If you use opioids in prescription drugs longer than intended, you are likely to become addicted and dependent on them. Opioids are considered narcotic drugs when abused and can easily lead to addiction, overdose, or death.
Signs and Symptoms of Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction is a major concern and can easily affect anybody in society. What’s more concerning about this type of addiction is that it affects both the individuals that are dependent on opioids and the people around them. Because the use of opioids causes health problems and behavioral changes in its users, opioid addiction hurts society.
Since prevention is better than cure, it is often advisable to look out for signs of opioid addiction in your loved ones. If you do notice any signs and symptoms of opioid addiction in your loved ones, you should help them seek out addiction treatment.
Opioid addiction affects your behaviors and actions, which makes it noticeable. It is crucial to spot the red flags. Early detection enables an individual to get the required assistance—including detox and further support to help the subject break off the dependence.
Below are some of the behavioral signs and symptoms of opioid addiction:
Mood and Personality Changes
You may experience personality changes when you are addicted to opioids. Personality changes due to drug abuse often include irritability, violence, and defensiveness. Those addicted to opioids even commonly fight with their family, friends, and even medical providers.
Poor Hygiene
Those struggling with opioid addiction often have lowered standards of personal hygiene. They fail to wash their clothes, take a bath, or maintain their appearance. Typically, opioid addicts shun social norms and are constantly in pursuit of these drugs.
Withdrawal
Opioid addicts tend to withdraw, especially from family, society, and social activities and occupations. Over time, opioid addicts begin engaging less and less in social activities. Depending on the stage of addiction, they may even withdraw from others completely.
Secrecy
People that struggle with opioid addiction tend to be very secretive about it. Opioid addicts will avoid talking about their addictions and will even become defensive when confronted about it. Opioid addicts will even turn violent in an attempt to cover up their addiction. However, controlling the addiction is tough, and the signs are apparent.
Low Concentration
People with opioid addiction tend to struggle to concentrate. Opioid addicts will experience difficulty focusing altogether. They may even struggle to stay awake or be attentive. These difficulties can affect their work and educational output.
Emotional Withdrawal
Opioid addicts will severely withdraw from others. They will even decline from emotional contact with family and friends. Moreover, opioid addicts will limit any close contact between themselves and other people out of fear of being judged. Emotional withdrawal is often attached to secretiveness.
Depression
Those who show signs of depression while suffering from opioid addiction have likely used drugs for an extended period. Even so, it’s standard for other types of disorders, such as PTSD and anxiety disorder, to be present while suffering from opioid addiction. Typically, depression signs can exist before drug abuse, but opioids heighten the issue because these addictive drugs can lead to mental health disorders.
Poor Decision Making
People with opioid addictions often make poor decisions and act recklessly. They can engage in high-risk behaviors such as having unprotected sex, driving while under the influence, stealing, and armed robbery. All these can lead to problems with authority, self-harm, and health problems.
Financial Problems Due to Borrowing
Financial stability is often a problem for opioid addicts. They borrow recklessly to satisfy their drug addiction. Opioid addicts also often skip work or get fired due to inconsistency and poor performance. All this leads to financial problems.
Below are some of the physical symptoms of opioid addiction:
- Signs of euphoria
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Nausea, constipation, and vomiting
- Slowed breathing
- Shrunken pupils
Opioid addiction can be severe, thus leading to an overdose. An overdose is dangerous and unforeseeable and can easily result in death. When you notice any of the following signs, seek help immediately:
- Limpness
- Muteness and inability to speak
- Unconsciousness
- Blue or Purple lips and fingernails
- Slowed heartbeat
- Extreme paleness
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Opioid Addiction?
Opioids are depressants and thus, work by slowing down the body’s movements and functions. The short-term effects of opioids are:
- Short and slow breath
- Drowsiness
- Unconsciousness
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Sometimes, one can slip into a coma
- Death due to the respiratory system and the heart fails to function
What are the Long-Term Effects of Opioid Addiction?
Prolonged abuse of opioids results in physical dependence and addiction. This addiction arises as a result of the subject’s body adapting to the presence of opioids in the bloodstream. Prolonged opioid use makes quitting difficult.
Opioid withdrawal symptoms occur if you reduce the number of opioids that you consume or stop taking opioids altogether.
Some opioid withdrawal symptoms include:
- Restlessness
- Insomnia
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Muscle, bone, and joint pains
- Shivering, especially when one quits cold turkey
Effects of Opioid Abuse on Mental Health
Opioid abuse affects over 2 million Americans, and the numbers keep growing. Opioid abuse hurts mental health. Those addicted to opioids often have mood and anxiety disorders, depression, and other psychiatric disorders. Having a mental health disorder can cause a person to stay dependent on opioids for a long time.
Opioid Abuse and Depression
Opioids contribute largely to depression. Research shows that around 10 percent of people that were prescribed opioids showed signs of depression within a month. Those who took opioids for a longer period showed an even higher percentage rate of depression.
There are several reasons why people with opioid addictions have mental health issues. For one, many people choose to abuse opioids as a form of self-medication. Self-medication is one way that people who are struggling with their mental health try to avoid their problems.
Through the chronic abuse of opioids though, these people start to develop a dependency or even an addiction. This only increases the severity of the mental health issues of opioid addicts as the chronic use of opioids messes with one’s brain chemistry. As a result, opioid misuse and mental disorders simultaneously advance one another over time by affecting the way the brain functions. Changes in the brain’s functionality can cause one to be depressed.
Opioid Addiction Treatment Options
Opioid misuse is a dangerous habit because it can take over your life and affect everyone surrounding you. When you notice signs and symptoms of opioid addiction, it’s good to get help.
There are several treatment options aimed at controlling opioid addiction. These include detoxification (detox), residential treatment (in-patient), and therapy treatment.
Detoxification
Detoxification is often the first step of opioid addiction treatment. It involves the elimination of opioids from your body and helps a person withstand the symptoms of withdrawal.
Detoxification is important because it opens doors for other treatment alternatives.
Reach out to North Jersey Recovery Center for high quality and safe opioid detoxification programs. We have medical professionals to help you overcome opioid addiction in a safe environment.
Residential Treatment
Residential treatment, also known as in-patient treatment, allows for the subject to receive opioid therapy in a safe environment. Residential treatment is the most effective treatment option because it requires you to reside in the medical facilities that you’re receiving treatment in. Residential treatment also provides 24-hour medical professional assistance.
Opioid addiction can be tough to overcome. It also has a high relapse rate. Fortunately, residential treatment provides medical professional care and assistance anytime that you need it. North Jersey Recovery Center provides a safe environment for your opioid addiction treatment with 24-hour professional assistance.
Therapy Options
Opioid misuse affects a subject’s physical and mental health. Opioid misuse even affects your behavior. When you abuse opioids for a long period, you develop a dependency, or worse, an addiction to it. To help treat an opioid dependency or addiction, therapy should be included in your treatment program.
Therapy focuses on your mindset. While in therapy for opioid addiction, you’ll learn ways to help you manage your addiction. That way you can minimize the chances of you relapsing.
There are two primary forms of therapy that your therapist will use to help you overcome your opioid addiction. These two forms of therapy are individual therapy and group counseling.
Individual Therapy
Individual therapy involves one-on-one conversations between you and a therapist. In individual therapy, you focus on self-development and self-introspection. Individual therapy helps you understand why you started abusing substances and how you can better manage your substance use triggers.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
While there are two primary forms of therapy used in addiction treatment, there are a variety of different types of individual therapy. One of the major types of individual therapy that gets used in addiction treatment is cognitive-behavioral therapy. Cognitive-behavioral therapy aims at changing one’s perspective on their addiction. It helps one rethink their actions and also manage stress.
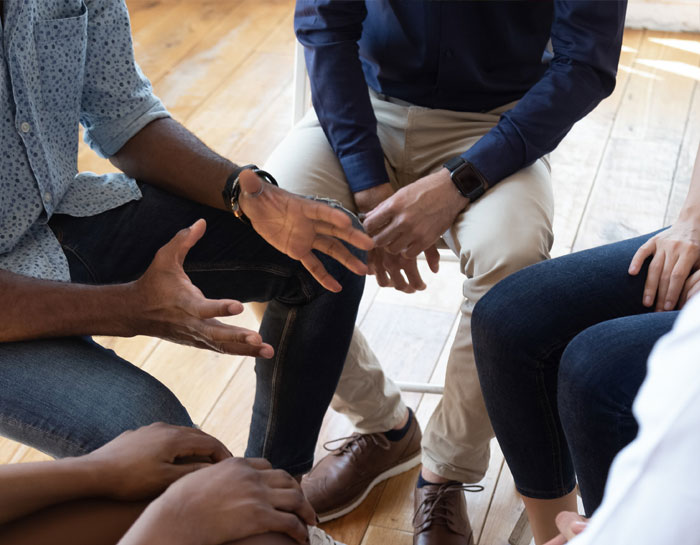
Group Counseling
Group counseling is when you and a group of other addicts meet up together with a therapist to learn from one another’s ups and downs in life due to addiction. During group counseling, you and the other addicts in the therapy session take turns sharing your experiences with substances.
North Jersey Recovery Center Is Here to Serve All Your Addiction Treatment Needs
North Jersey Recovery Center is an addiction treatment center located in New Jersey. Established to help people with drug and alcohol addiction, our institution aims to help rehabilitate those dealing with opioid addiction through the use of long-term recovery plans.
To learn more about our treatment services, contact us here.